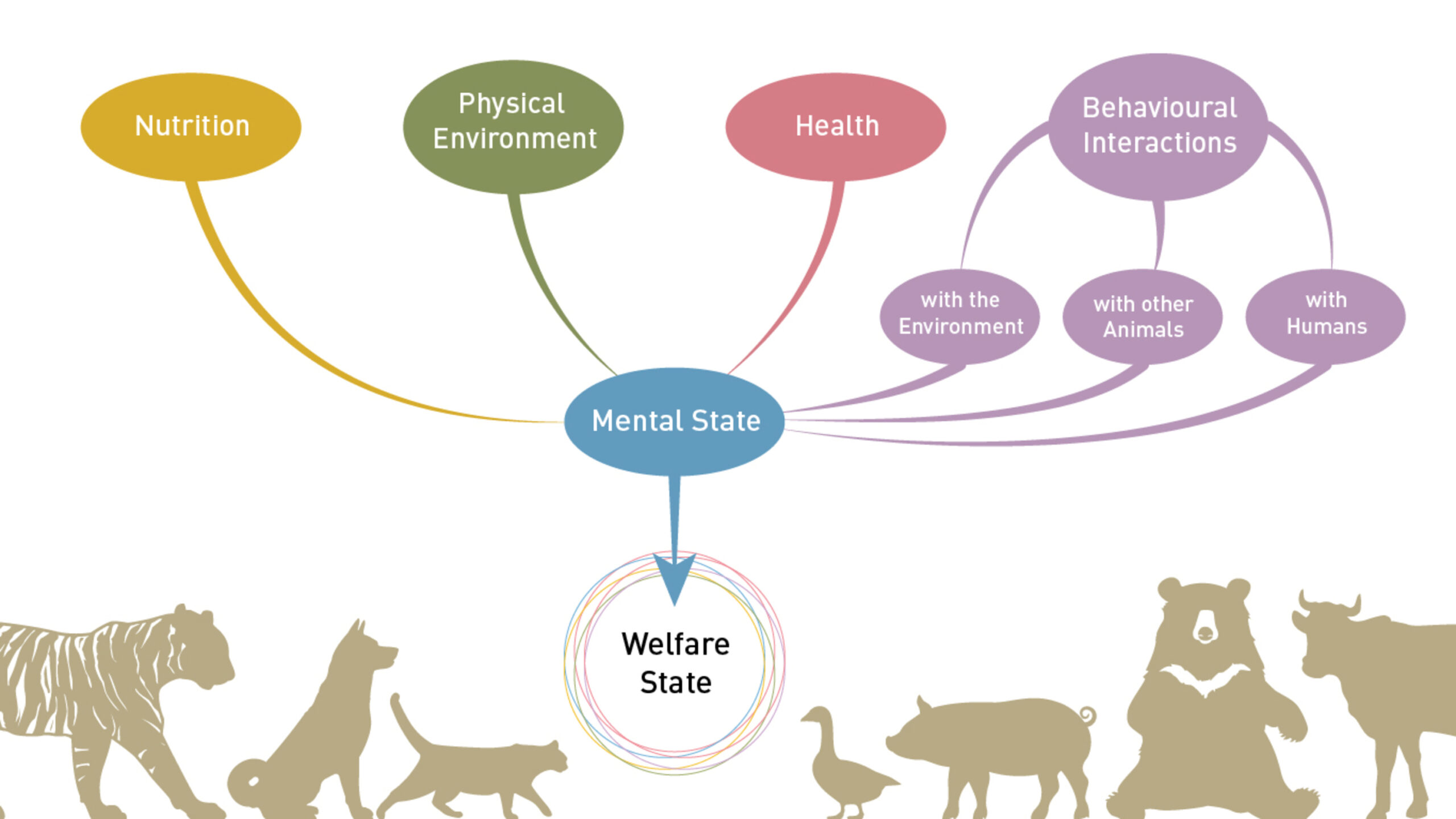
Animal welfare, often relegated to secondary status in the grand scheme of global priorities, merits foremost attention due to its far-reaching implications on ethical, environmental, and socio-economic dimensions. In an increasingly interconnected world, the moral obligation to enhance animal welfare transcends cultural boundaries, urging nations to prioritize humane treatment and protection for all sentient beings. This article delves into the compelling reasons why enhancing animal welfare should be regarded as a global priority.
To understand the complexities of animal welfare, one must first appreciate the moral imperatives underlying this movement. Many philosophical frameworks, from utilitarianism to deontology, recognize the intrinsic value of sentient beings and the responsibility humans bear to mitigate suffering. Animals, as sentient beings capable of experiencing pain and joy, deserve lives free from cruelty and neglect. This ethical perspective necessitates reassessing our relationships with animals, acknowledging them as companions or kin rather than mere commodities or resources.
Furthermore, the concept of ** interconnectedness** underscores the relevance of animal welfare within global ethics. The health of ecosystems relies heavily on the welfare of non-human animals. Biodiversity is paramount to ecological balance; when animal populations decline due to human-induced factors such as habitat destruction, poaching, or industrial farming practices, ecosystems suffer. The degradation of environment translates into socio-economic decline, affecting human communities reliant on nature for their livelihoods. Thus, prioritizing animal welfare is an effective means of preserving not only wildlife but also human welfare and sustainability.
Moreover, addressing animal welfare aligns with pressing global challenges such as climate change. The agricultural sector, particularly industrial livestock production, is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. By improving animal welfare standards, countries can shift towards sustainable practices that reduce the carbon footprint of food production. Alternatives such as plant-based diets and regenerative agriculture present viable solutions that benefit both animals and the environment. Thus, increasing animal welfare is not merely an ethical consideration; it is a pragmatic approach to combating climate change.
In addition to environmental considerations, there are tangible economic benefits associated with improved animal welfare practices. Farmers who adhere to higher welfare standards can experience enhanced productivity and profitability. Healthier animals yield better-quality products, leading to market advantages. Additionally, as consumer awareness regarding ethical animal treatment rises, there is a growing demand for responsibly sourced products. By embracing higher standards, businesses can cater to ethical consumerism, ensuring their economic viability in a competitive market while contributing to a positive change.
Despite the clear benefits, significant challenges impede the advancement of animal welfare on a global scale. Varying cultural perceptions of animals often clash with the universal concept of animal rights. Some cultures view animals primarily as resources for labor, food, or entertainment. This divergence complicates international cooperation on welfare initiatives, necessitating thoughtful discourse that respects cultural diversity while advocating for fundamental improvements in the treatment of animals. Education is imperative in fostering understanding and empathy, and tailored strategies must be adopted to engage different societies in this vital conversation.
To combat these challenges, collaboration among governments, non-governmental organizations, and the private sector is essential. Multi-stakeholder partnerships can propel the enforcement of humane policies and standards that transcend national borders. For example, organizations like FOUR PAWS work tirelessly to advocate for improved animal welfare regulations worldwide and offer guidance to countries striving to elevate their standards. Such collaborative efforts can bring about innovative solutions that address local needs while contributing to global goals.
Moreover, fostering a culture of compassion and empathy towards animals begins early in a society’s educational framework. Integrating animal welfare education into school curricula can instill values that prioritize humane treatment from a young age. By teaching children about the emotional lives of animals and the consequences of neglect and cruelty, societies can cultivate a new generation of conscientious citizens committed to seeking positive change.
The role of technology in enhancing animal welfare cannot be overlooked. Advancements in animal monitoring and health management technologies are revolutionizing the way we care for animals. Innovations such as precision farming and animal tracking systems enable farmers to maintain a closer watch on animal welfare, promptly addressing illnesses or behavioral issues. This integration of technology paves the way for more humane treatment and can significantly improve overall welfare standards.
In conclusion, increasing animal welfare should unequivocally be a priority on the global agenda. The interconnectedness of animal welfare with ethical responsibilities, environmental sustainability, economic viability, and cultural understanding highlights its multidimensional significance. By prioritizing animal welfare, nations not only uphold moral values but also foster healthier ecosystems, resilient economies, and compassionate societies. The world stands at a critical juncture, and the choices made today regarding animal welfare will indelibly shape the future for all sentient beings. A concerted effort toward improving animal welfare signifies a commitment towards a more compassionate, sustainable, and ethical world.